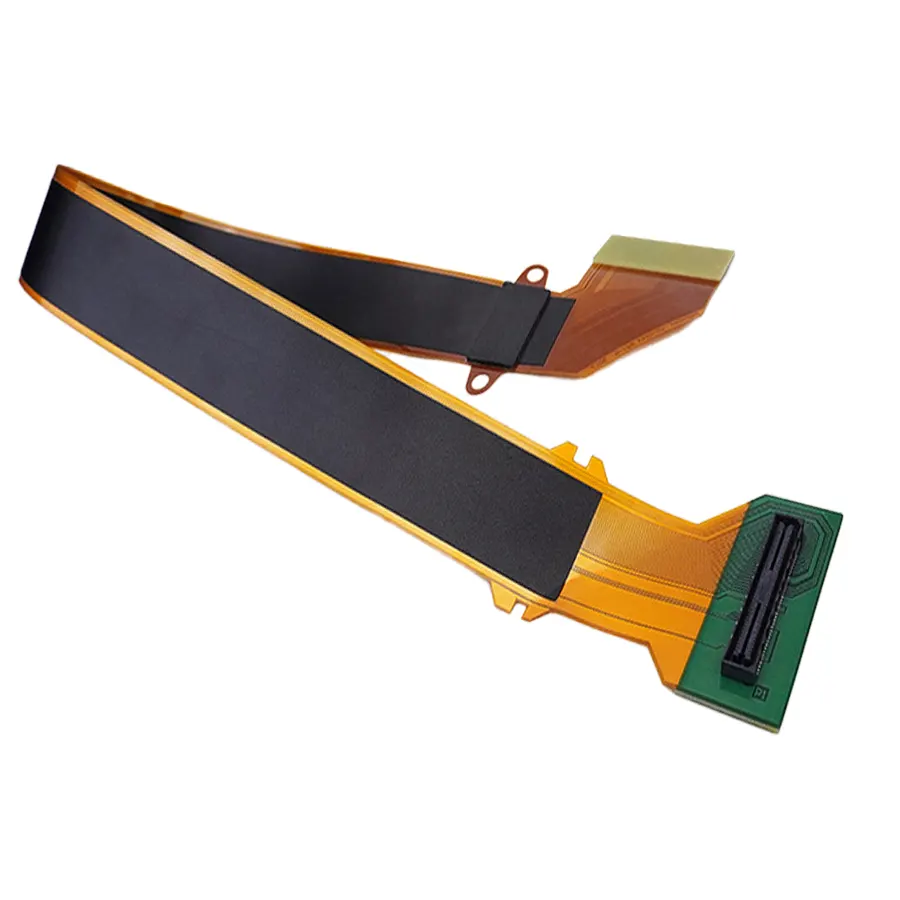
The Role of FPC Connectors in Transfer FPC Design and Applications
Introduction
Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs) have revolutionized electronic designs with their flexibility, compactness, and reliability. Among their various types, Transfer FPCs stand out for their critical role in connecting mainboards to functional boards in devices. A key component enabling this functionality is the FPC connector, which ensures secure, high-density, and efficient connections. This article explores the importance of FPC connectors in Transfer FPC design, their applications, and the challenges associated with their production.
FPC Connectors: The Backbone of Transfer FPCs
An FPC connector serves as a bridge between flexible printed circuits and other electronic components. Its role is particularly crucial in Transfer FPCs, where reliable and compact connections are essential.
Key Features of FPC Connectors
- Compact Design: Enables high-density connections in space-constrained devices.
- Versatility: Supports both static and dynamic applications, making it suitable for diverse industries.
- Ease of Assembly: Designed for quick and reliable integration, reducing production time and costs.
Applications of Transfer FPC with FPC Connectors
Transfer FPCs integrated with FPC connectors are widely used in devices requiring modularity and flexibility. Some examples include:
- Consumer Electronics
- Smartphones and tablets use Transfer FPCs to connect mainboards to functional boards, such as cameras or fingerprint modules.
- In laptops and printers, they link motherboards to display panels or control buttons.
- Automotive Electronics
- Modern vehicles rely on Transfer FPCs for connecting infotainment systems, control panels, and advanced sensors.
- Industrial Equipment
- Printers and scanners utilize Transfer FPCs for reliable connections under heavy-duty operations.
Design Considerations for Transfer FPC with FPC Connectors
Transfer FPC design requires careful consideration of its connection methods and materials:
Connection Methods

BTB connector

ZIF connector
- FPC Connector-Based Connections
- BTB Connectors: Used for board-to-board connections, offering high-speed data transfer.
- ZIF Connectors: Popular for easy assembly and maintenance.
- Direct Soldering
- Provides permanent connections but limits flexibility for repairs or upgrades.
Layer Configuration
- Multi-layer Transfer FPCs can support up to 16 layers.
- For interference-prone environments, adding a grounded mesh layer helps mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Material Selection
- Electrolytic Copper: Suitable for static applications, offering cost efficiency.
- Rolled Copper: Preferred for dynamic environments due to its superior durability.
The Advantages of FPC Connectors in Transfer FPCs
When paired with FPC connectors, Transfer FPCs offer unparalleled benefits:
- Space Optimization: Their compact design is ideal for slim, lightweight devices.
- Design Flexibility: Support for multi-layer designs allows customization to meet specific requirements.
- Improved Performance: The reliable connection methods ensure consistent performance, even in dynamic environments.
Conclusion
The integration of FPC connectors in Transfer FPCs has redefined how electronic devices achieve compactness and reliability. From consumer electronics to automotive systems, their applications continue to grow, driven by advancements in design and production techniques. By addressing challenges such as high-density soldering and EMI shielding, manufacturers can harness the full potential of FPC connectors to create innovative and efficient devices.
Learn about others
What is the FPC connector? https://components.omron.com/us-en/products/connectors/board-to-fpc-connectors/board-to-fpc-connector_features
What is the BTB connector?: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Board-to-board_connector








Leave A Comment