PCB Manufacturing Services: A Guide to the Production Process
Introduction
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a crucial component of electronic devices, serving to connect and mechanically support the electrical functions between various electronic components. In the manufacturing process of electronic products, the production and fabrication of PCBs is a critical step. So, what are the processes and key aspects involved in PCB Manufacturing Services?

Order Processing
The first step in PCB manufacturing is order processing. It is critical to thoroughly review the order to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the customer’s PCB design requirements. This includes verifying the integrity and correctness of the design files and confirming the correct version. Any discrepancies or questions are promptly addressed with the customer. The order details are then entered into the production planning and scheduling system, ensuring that the manufacturing capabilities meet or exceed customer expectations.
CAM Tooling
The next phase involves the use of Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) tools. During this stage, the design files are scrutinized to confirm the correct release version and part numbers. The PCB CAD layout undergoes rigorous design rule checks (DRC) to identify and resolve any potential issues affecting manufacturability and quality. Drawing from extensive experience in PCB assembly, we meticulously review the design for Design for Manufacturability (DFM) considerations. Any concerns are communicated to the customer and resolved accordingly. Production tooling, including drill files, routing, copper layers, solder masks, and legend layers, is generated with the appropriate processing frames and step-repeat patterns. These data files are stored in a tool database under a unique tool number, guiding the entire PCB production process.
Rational PCB Design
A well-structured PCB design is fundamental to minimizing signal interference and loss. During the PCB design phase, efforts are made to reduce trace lengths and avoid cross-talk and signal attenuation. Additionally, the layout should be carefully partitioned, with thoughtful pin assignments to facilitate signal transmission and soldering. Proper spacing between pins and components is crucial to minimize interference and ensure tolerance levels.
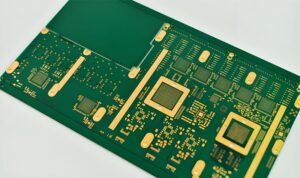
Material Selection and PCB Thickness
The choice of materials for the PCB significantly impacts the performance and reliability of the final electronic product. Common materials include FR-4, aluminum substrates, and ceramic substrates, each offering distinct thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and mechanical strength characteristics. The material must be selected based on the specific requirements of the product. Similarly, the PCB’s thickness should be determined according to the product’s specifications and manufacturing processes, balancing durability with performance needs.
PCB Manufacturing Processes
The PCB manufacturing process encompasses several critical techniques, including printing, gold plating, chemical etching, and surface-mount technology (SMT). The printing process requires the selection of suitable printing machines, inks, and printing plates to ensure high-quality results. The gold plating must utilize appropriate metal materials and electroplating methods to enhance the PCB’s conductivity and corrosion resistance. Chemical etching demands precise control over the etchant composition and application to achieve accurate circuit patterns. The SMT process involves choosing the correct pick-and-place machines and soldering materials to ensure the precision and reliability of component placement.
Quality Control and Testing
Quality control is an ongoing process in PCB manufacturing services, encompassing first-article inspection, process control, and final inspection. First article inspection involves producing and testing a sample before mass production to confirm the process’s accuracy and feasibility. Process control refers to implementing effective measures throughout production to maintain product quality and efficiency. Final inspection includes comprehensive testing and examination of the finished PCBs to ensure they meet all functional and quality standards.

Conclusion
Mastering the PCB manufacturing process requires a deep understanding of various techniques and meticulous attention to detail. From rational design and material selection to process control and quality assurance, each step plays a pivotal role in ensuring the production of high-quality PCBs. By focusing on these key elements, manufacturers can achieve excellence in PCB production, delivering products that meet the highest standards of performance and reliability.







Leave A Comment