What is a rigid flex circuit board?
Introduction
With the development of The Times, the application of circuit boards is more and more extensive. Rigid-flex PCBs combine the best features of both rigid and flexible printed circuit boards, providing manufacturers with the ability to install circuits in confined spaces with ease. This added flexibility allows for precise and effortless manipulation during installation, making rigid flex circuit boards a versatile solution in various applications.

What is a Rigid-Flex PCB?
As the name suggests, rigid flex circuit boards are a hybrid of flexible and rigid ones. These designs offer unique solutions and applications that can often replace traditional rigid PCBs. One of the greatest advantages of rigid-flex PCBs is their ability to combine the strengths of both flexible and rigid PCBs, creating a versatile and efficient circuit solution.
Advantages of rigid flex circuit boards
By combining the characteristics of rigid and flexible PCBs, rigid-flex PCBs offer numerous benefits to both manufacturers and consumers.
1. Mechanical Stability
Rigid-flex PCBs are composed of alternating layers of rigid and flexible PCB materials. This structure ensures that they are both stable and flexible, making them easy to install in confined spaces.
2. Reliable Connections
Rigid-flex PCBs provide enhanced stability and polarity, simplifying and securing connections with other components. Additionally, fewer connector components are required for each application.
3. Dynamic Flexibility
In addition to repeatability and precision, rigid-flex PCBs offer greater packaging flexibility, accommodating complex and compact designs.
4. Cost Efficiency
Utilizing rigid flex circuit boards can reduce overall expenditures by minimizing the need for additional components and simplifying assembly processes.
5. High-Density Applications
Arguably, the most significant benefit of rigid-flex PCBs is their suitability for high-density device clusters. Their flexibility, stability, and minimal space requirements make them ideal for such applications.
6. High Impact and Vibration Resistance
Electronic components are used in a wide range of items, some of which are subjected to continuous vibration. With rigid flex circuit boards, you don’t have to worry about damage, as they possess strong resistance to both impact and vibration.
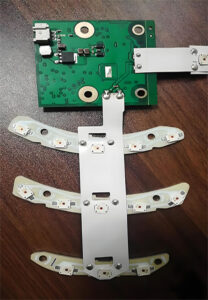
Rigid-Flex PCB Design Guidelines
When transitioning to rigid-flex PCB design, several factors must be considered—some of which may be new to you. These include:
1. Layer Count Considerations
Rigid-flex PCBs are made from alternating layers of flexible and rigid PCB materials. Before making the transition, determine how many layers your intended application requires. Consult your original equipment manufacturer (OEM) to ensure they can meet these requirements.
2. Thermal Management
When current flows through electronic devices, heat dissipates. The amount of heat released depends on factors such as device characteristics, power, and PCB design. As heat increases, it can affect device performance and potentially cause damage. Take measures to reduce heat dissipation.
PCBs within devices should facilitate heat dissipation. This can be achieved by adhering to rigid-flex PCB design guidelines.
3. Material Stack-Up
For rigid-flex boards, material stack-up is a critical factor. Achieving optimal stack-up requires close collaboration with your manufacturer on the following aspects: UL flammability rating, appropriate materials, minimum bend radius requirements, RoHS certification, impedance control, mechanical considerations, and lead-free assembly compatibility.
Material stack-up significantly impacts cost, performance, and manufacturability. Invest sufficient time and resources into finding the best stack-up. Once the appropriate model is developed, have your designer perform the necessary calculations, followed by validation by the manufacturer.
It is possible to use boards with different layer counts. For example, one board may have 20 layers, while another has 12 layers. However, they must have similar stack-ups, and thicknesses and adhere to rigid-flex PCB design rules. This will help minimize manufacturing issues that could derail your project.
Rigid vs. Flex PCBs: Which is Better?
The debate between rigid PCBs and flexible PCBs has been ongoing for some time. To determine which is ideal, it is best to understand how they compare.
Firstly, rigid PCBs are the standard type of PCBs most people think of when they think of circuit boards. They use conductive tracks and other components arranged on a non-conductive substrate to connect electronic components. Typically, the non-conductive substrate also contains glass to make the board more robust. In addition to providing strong support, rigid circuit boards offer excellent heat resistance for electronic components.
Apart from the rigidity and base materials, there are also some notable differences between flexible and rigid PCBs. These include:
– Manufacturing Process: Rigid PCBs are made using a solder mask. However, for flexible PCB designs, a process known as overlay or overlay is used. This ensures the protection of the exposed circuits on the flexible PCB.
– Conductive Material: Unlike rigid PCBs, flexible PCB boards should be able to bend. To achieve this characteristic, flexible rolled annealed copper is used instead of electro-deposited copper as the conductive material.
– Cost: Rigid PCBs are less expensive than flexible circuit boards. However, if you need a PCB that can be installed in compact spaces, you should be willing to bear the cost of flexible PCBs.

How Rigid-Flex PCBs Benefit Your Applications
Both rigid and flexible PCBs have unique features that are invaluable for specific applications. However, you are not necessarily limited to just one. To benefit from the characteristics of both, switch to rigid-flex PCBs. In summary, the benefits of rigid-flex boards include:
– Cost efficiency
– Reduced packaging weight
– Simplified assembly
– The ability to withstand hundreds of bend cycles
– Increased circuit density
Conclusion
rigid flex circuit boards offer a comprehensive solution by merging the strengths of rigid and flexible PCBs. From enhancing mechanical stability to reducing overall costs, the benefits are clear. By following proper design guidelines, such as considering layer count, managing heat, and carefully selecting material stack-up, you can optimize the performance of your rigid-flex PCB designs. For cutting-edge technology and reliable manufacturing, trust Gekunflex to meet your rigid-flex PCB needs.

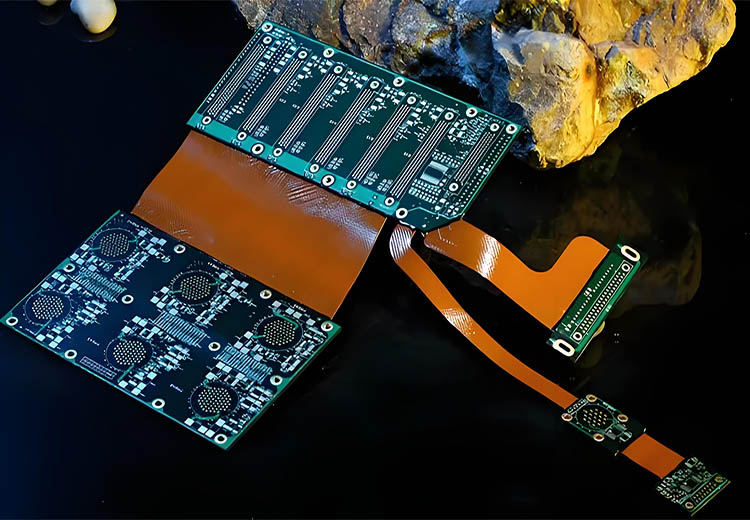

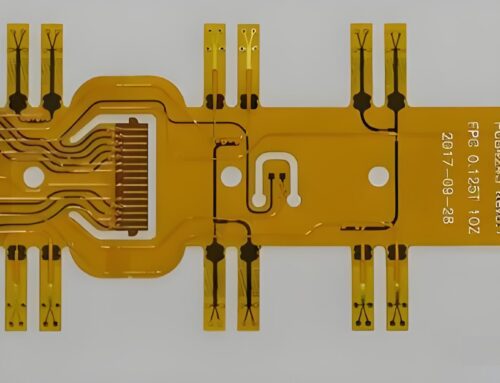




Leave A Comment