Multilayer Flexible PCBs: Market Trends and Applications
Introduction
Multi-layer Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (Multilayer Flexible PCBs) are vital components in modern electronic products. Made from flexible substrates such as polyimide film, these boards exhibit flexibility, allowing them to bend, fold, and twist without affecting functionality. FPCBs consist of multiple circuit layers, insulating layers, and cover layers, interconnected to achieve complex circuit functions. Widely used in smartphones, tablets, laptops, digital cameras, and medical devices, FPCBs offer significant advantages, including compact size, lightweight, and flexibility, making them indispensable in contemporary electronics.
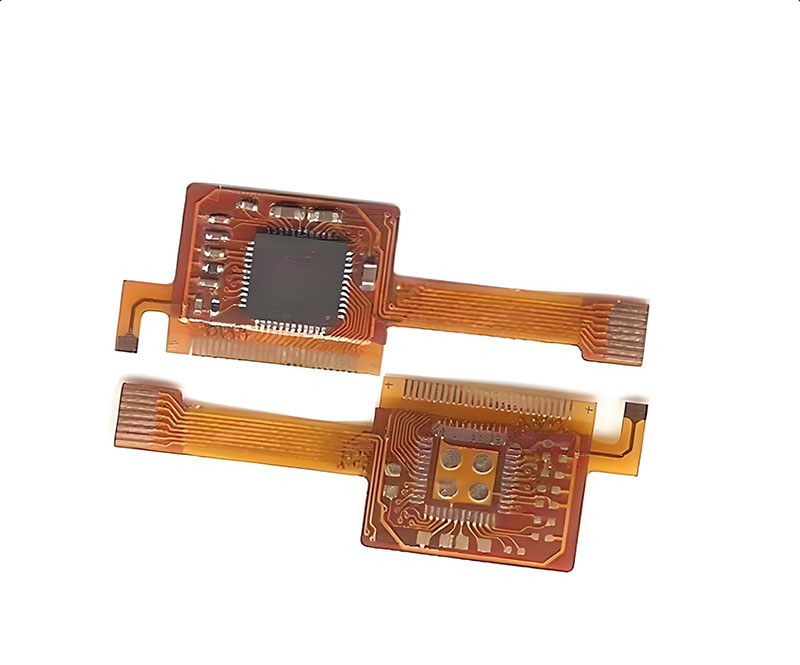
Overview of Multi-Layer Flexible Printed Circuit Boards
Multi-layer FPCBs are constructed from several layers of flexible materials and circuit layers. Typically, these boards consist of three to six circuit layers, interspersed with insulating layers and covered with protective or copper layers. This structure provides high reliability, fault tolerance, and stability, making them essential in high-performance electronic products.
Key Segments of the Multi-Layer FPCB Industry Chain
Substrate Production
The initial step in the multi-layer FPCB industry chain involves producing flexible substrates, primarily using polyimide films. The quality of these substrates directly impacts the performance and durability of the final FPCBs.
Printing Process
The printing process is the core segment of the multi-layer FPCB industry chain. This includes the design, printing, and formation of circuit patterns, ensuring the FPCBs’ reliability and efficiency.
Surface Treatment
Surface treatment is crucial, involving processes such as chemical copper plating, gold plating, and tin plating. These treatments enhance the conductivity of circuit layers and protect them from environmental damage, thereby extending the FPCBs’ lifespan.
Assembly
The final step is assembly, encompassing soldering, component placement, and testing. This step integrates multi-layer FPCBs with other electronic components, ensuring their functionality and reliability.

Major Advantages of Multi-Layer FPCBs
Superior Transmission Performance
Multi-layer FPCBs offer higher transmission performance, as they can transmit more signals within a small area. This capability enhances the overall performance of the circuit.
Higher Circuit Density
The ability to stack circuit layers significantly increases circuit density, improving complexity and functionality while reducing circuit size.
Enhanced Reliability
The even and balanced distribution of circuit layers within multi-layer FPCBs reduces stress during operation, increasing reliability and stability.
Optimized Space Utilization
The tightly packed internal structure of multi-layer FPCBs optimizes circuit design, allowing different components to be stacked together, enhancing space utilization, and reducing overall circuit size.
Challenges of Multi-Layer FPCBs
High Manufacturing Cost
The production of multi-layer FPCBs involves intricate printing and assembly techniques, making manufacturing difficult and costly.
Complex Termination Methods
The termination methods for multi-layer FPCBs are more complex than single-layer boards, requiring folding and inter-layer connections, which increases manufacturing difficulty.
Applications of Multi-Layer FPCBs
Automotive Electronics
They are widely used in automotive internal electronic systems, such as air conditioning, navigation, and audio systems.
Communication Devices
They are increasingly used in communication devices like smartphones and tablets.
Industrial Control Systems
Provide high-performance solutions for industrial control systems, such as manufacturing automation and robotics.
Medical Equipment
Extensively used in medical devices, including medical instruments and life monitoring equipment.

Conclusion
The multi-layer flexible printed circuit board market presents vast growth and innovation opportunities. As electronic devices continue to develop, the demand for miniaturized, lightweight, and flexible circuit solutions will persist. Investors and industry participants must stay abreast of market trends and technological advancements to harness the potential in this dynamic market.






Leave A Comment