The Evolution and Advancements in PCB Solder Mask Ink
Introduction
In producing Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), PCB Solder Mask Ink is crucial in enhancing soldering efficiency and protecting areas that do not require soldering from damage. The development of PCB ink is closely intertwined with advancements in equipment technology, soldering conditions, and circuit requirements.

Low Viscosity Inkjet Solder Mask Ink
As the electronics industry progresses, a fully additive electronic technology employing inkjet printing has emerged, offering benefits such as material savings, environmental protection, and process simplification. This new technology places specific demands on the properties of the ink and substrate materials, which are:
– Controlling Ink Viscosity: Ensuring the ink can be continuously ejected through the nozzle without clogging.
– Regulating Curing Reaction Speed: Achieving rapid initial curing to prevent ink from spreading on the substrate due to wetting.
– Adjusting Ink Thixotropy: Ensuring the quality and repeatability of printed circuits.
The development of low-viscosity solder mask ink focuses on modifying traditional solder mask materials and using active or inactive agents to meet these new requirements.
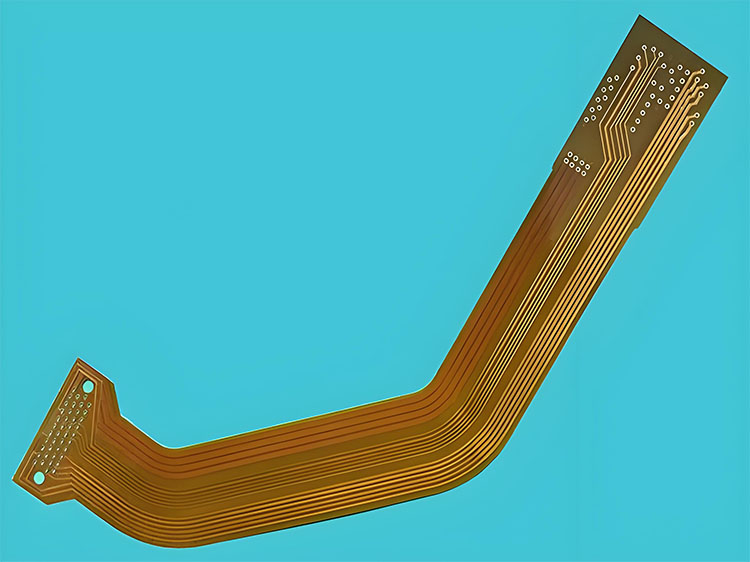
Solder Mask Ink for Flexible Printed Circuits (FPC)
With the rapid growth of the PCB industry, the demand for FPCs has significantly increased, requiring new material properties. The copper conductors on flexible boards are highly susceptible to oxidation, making the solder mask materials for flexible boards a research hotspot. Traditional epoxy-based solder mask films exhibit high brittleness after curing, unsuitable for flexible boards. Thus, integrating flexible chain segments into traditional resin structures while maintaining original solder mask properties is key. The resulting ink offers excellent storage stability and dissolves well in sodium carbonate and ammonia solutions. Its cured film meets mechanical, thermal, and acid-alkali corrosion resistance requirements.
Water-soluble alkaline Developer Photodefinable Solder Mask Ink
To reduce the emission of organic solvents in PCB manufacturing and mitigate their environmental impact. The development of solder mask ink has shifted from organic solvent-based processes to dilute alkaline water developers, and recently to water-based development techniques. Additionally, to meet the requirements of lead-free soldering technology. There has been a focus on enhancing the high-temperature resistance of the solder mask layer.
Conclusion
The evolution of PCB solder mask ink from dry film and thermosetting types to UV-curable and photo-definable solder mask inks highlights the continuous advancements in the field. The development of low-viscosity inkjet solder mask ink, FPC-specific solder mask ink, and water-soluble alkaline developer photo-definable solder mask ink showcases the industry’s response to the increasing demands for higher-density PCBs and lead-free soldering processes. These innovations not only improve the efficiency and quality of PCB manufacturing but also contribute to environmental sustainability.






Leave A Comment