FFC vs FPC: Which One Fits Your Design Best?
1. Introduction
Flexible electronics have changed how we design modern devices. They are especially useful in batteries. These electronics save space and provide high-performance electrical connections. FFC (Flexible Flat Cable) and FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) flexible interconnects are among the most commonly used.
Although they appear to be quite similar at a glance, their structures, functions, and uses vary greatly. Here, we detail the main distinctions between FFC and FPC, helping you to determine which is the right choice for you.
2. Understanding the Basic Structures
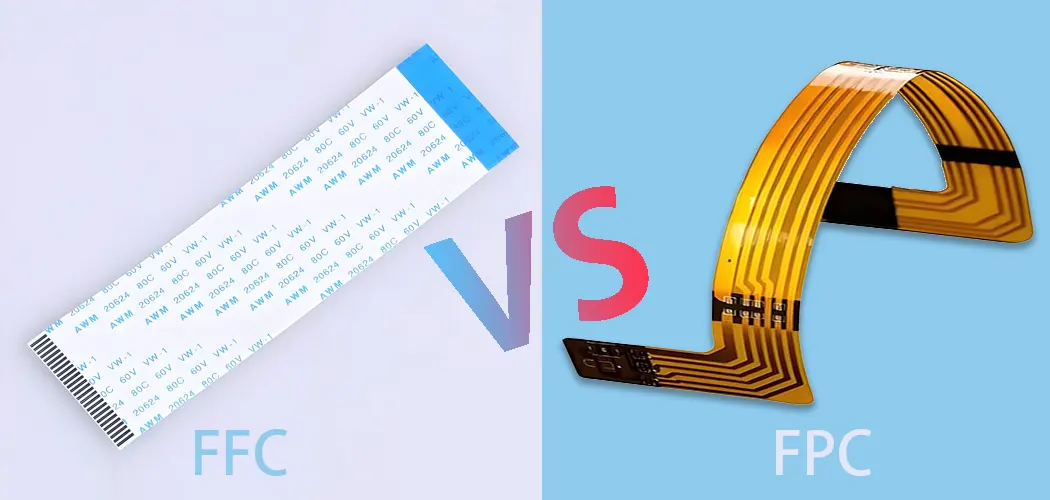
What is FFC?
FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) is a flat cable. It has many metal conductors lined up next to each other. Manufacturers make the cable from a thin, flexible plastic film, usually PET plastic.
Manufacturers often use flex-type electrical cables in devices like laptops and printers. People need them for high flexibility in small spaces. I.e., Standardized pitch sizes of 0.5mm, 1.0mm, and 2.54mm; Features flat flexible cables with consistent insertion force.
What is FPC?
A Flex PCB (FPC), also known as FPC cable, refers to a printed circuit board that engineers configure using flexible materials, including polyimide. It has one or more conductive layers, usually made of copper. These layers can be single-sided, double-sided, or multilayer.
You can make these printed circuits using various materials on flexible surfaces. You can arrange them in any layout. They meet the needs of thin and complex designs found in consumer electronics, medical devices, and cars.
3. What is the difference between FFC and FPC?
Comparison Table
| Feature | FFC | FPC |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Flat flexible cable | Etched printed circuit |
| Material | PET, copper conductors | Polyimide, copper layers |
| Layers | Single conductor layer | Single sided, double sided, multilayer |
| Design Flexibility | Limited to straight paths | Fully customizable |
| Pitch Sizes | 0.5mm, 0.8mm, 1mm, 1.25mm, 2.54mm | Custom; down to 0.05mm |
| EMI Shielding | Metal foil wrapping | Shielding film + ground connection |
| Connectors | ZIF | ZIF, BTB |
| Cost | Lower | Higher, varies by complexity |
| Common Applications | Flat connections in electronics | High-performance, flexible circuit boards |
① Manufacturing Techniques
FFC is produced through stamping or lamination, where pre-manufactured flat metal conductors are laminated between PET layers. Light-based printing and chemical etching manufacture FPCs, allowing for complex circuit layouts.
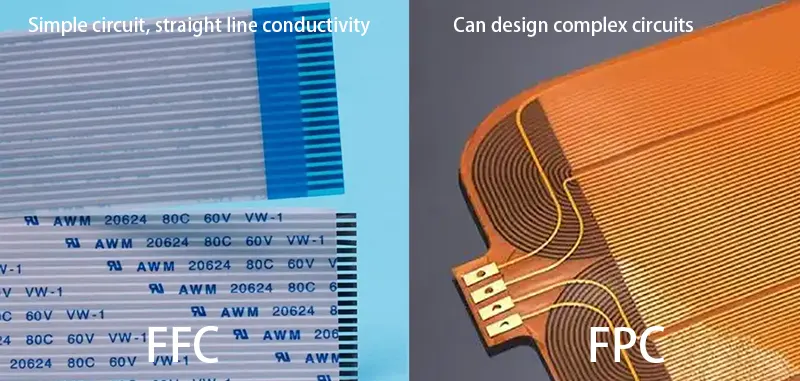
② Design Flexibility & Conduction Mechanism
- FFC is inherently linear—the conductors run straight without the ability to cross over or create multilayered paths. Designers mostly restrict it to single-conductor layer designs. Typical pitch options include 0.5mm, 0.8mm, 1mm, 1.25mm, and 2.54mm. The shapes and lengths are limited, offering fewer personalized designs for unique device designs.
- FPC, in contrast, allows for creative and compact layout designs with intricate routing. It supports side-flex circuits. This means you can place circuits on single side, both sides, or stack them in multilayer flexible PCB setups. You can make the trace width and spacing as fine as 0.05mm to accommodate high-density applications.
③Electrical and Mechanical Performance
FPCs generally offer better performance in terms of signal integrity and thermal resistance due to high-quality materials and superior design flexibility. FFCs, while simpler, are still highly effective for short, fixed routing.
④ EMI Shielding Capabilities
- FPC manages EMI shielding by using metal films on both sides. It grounds them through vias, making it efficient and low-cost.
- FFC requires you to wrap the whole cable in metal foil. Then, you must insulate it with a non-conductive layer. This is a labor-intensive process, slower to produce and more expensive overall.
⑤ FFC FPC connector
- FFC typically uses ZIF (Zero Insertion Force) connectors.
- FPCs, by contrast, support ZIF as well as BTB (Board-to-Board) connectors, giving more options in compact or modular system design.
Details of commonly used connector manufacturers: OCN \ HRS \ KYOCERA
⑥ Cost Considerations
FFC tends to be cheaper due to simpler manufacturing and materials, especially in high-volume applications. FPC can be more expensive but offers greater functional value and design freedom.
⑦ Application Differences
| FFC Applications | FPC Applications |
|---|---|
| Printers, LCDs, laptops | Smartphones, tablets, medical devices |
| Consumer appliances | Automotive sensors and battery packs |
| Optical drives | Wearables and IoT devices |
| Internal wiring between fixed boards | Flexible antennas, curved PCB applications |
4. How to Choose Between FFC and FPC
The right choice depends on your application requirements:
- FFC flat flexible cable is a great choice if you want to add easy, low-cost flat cable connections to your design. It works well for a standard layout.
- Flexible printed circuits (FPC) are more versatile than FFC high-density routing, and performance-demanding applications, such as smartphones. Also, dimensions, power requirements, mechanical stress, and the connector work with. Talking to a flex PCB manufacturer or flexible circuit board manufacturer early in the design process is helpful. It can save both time and money.
5. Conclusion
Both FFC and FPC serve essential roles in modern electronics. FFC(flat flex cables) is simple and affordable. FPC allows for advanced designs and more tailoring.
Knowing the difference helps you make better choices. This leads to improved product performance, easier manufacturing, and lower costs.
If you are using diy flexible PCB. Understanding them can help you make better design choices. This applies to flex PCB projects and sourcing from rigid flex PCB manufacturers.






Leave A Comment