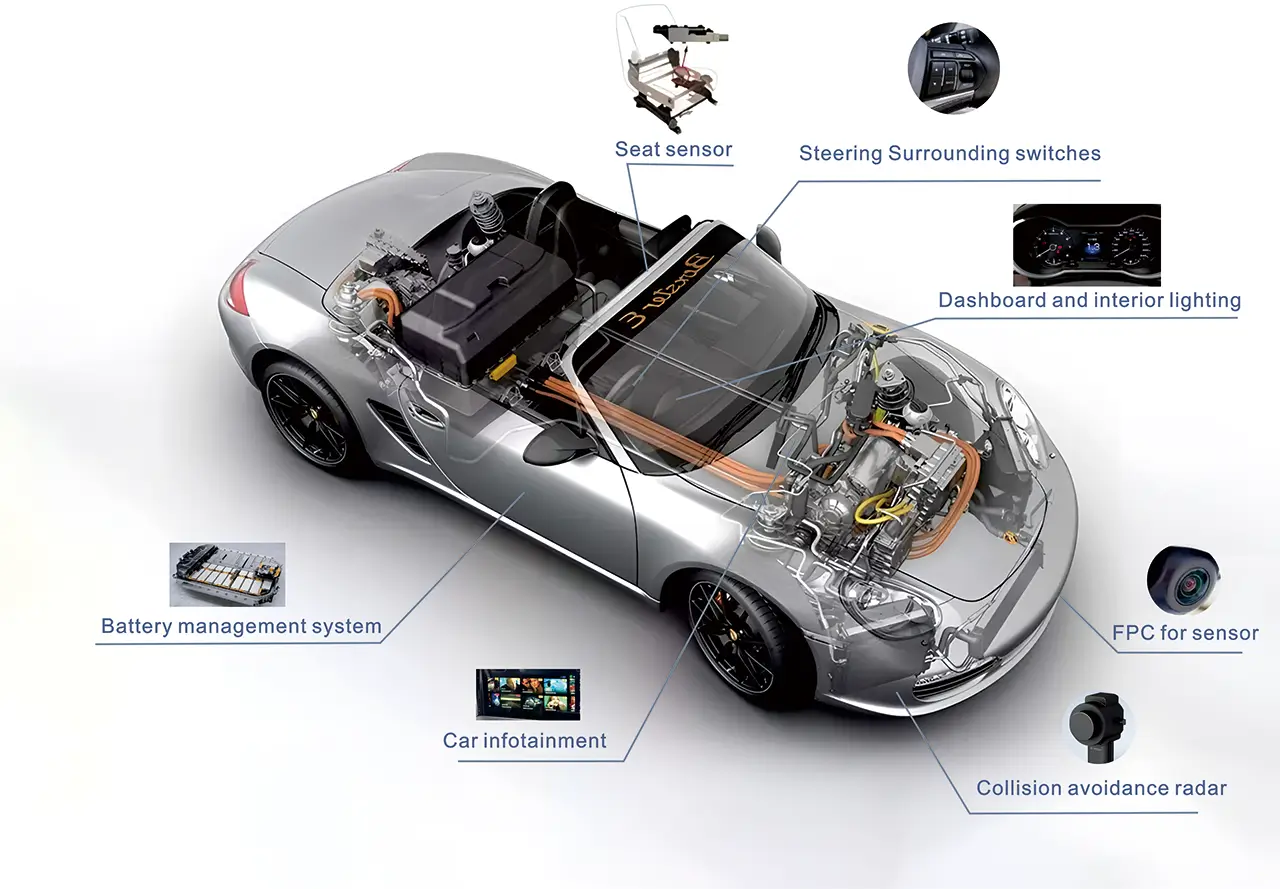
Flexible Circuit Boards in Automotive Electronics
Why Automotive Electronics Must Use Flexible Circuit Boards: 3 Essential Advantages
Comparison Table: Rigid PCB vs Flexible Circuit Board
| Feature | Rigid PCB | Flexible Circuit Board |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight designs |
| Space Utilization | Limited | 3D routing capability |
| Vibration Resistance | Poor | Excellent (vibration-resistant FPC) |
| Temperature Tolerance | Moderate | High (high-temperature resistant FPC) |
| Cost Over Lifecycle | Higher (due to failures) | Lower (durability) |
Key Advantages:
Three-Dimensional Routing Capability
Flexible PCBs allow complex 3D configurations, essential for automotive high-density interconnects and space optimization.
Stability Under Harsh Environments
With thermal management features and resistance to vibrations, FPCs ensure reliability and durability in extreme driving conditions.
Weight Reduction and Cost Efficiency
Flexible circuit allows lightweight EVs to enhance energy efficiency and decrease the complexity of wiring.
9 Critical Applications of Flexible Circuit Boards in Automotive Electronics
① Vehicle Displays and Touch Modules
Flex circuits enable sleek, curved displays for better aesthetics and user experience.
② ADAS Sensors and Automotive Radar Systems
FPCs provide precise connections for safety-critical sensors and cameras.
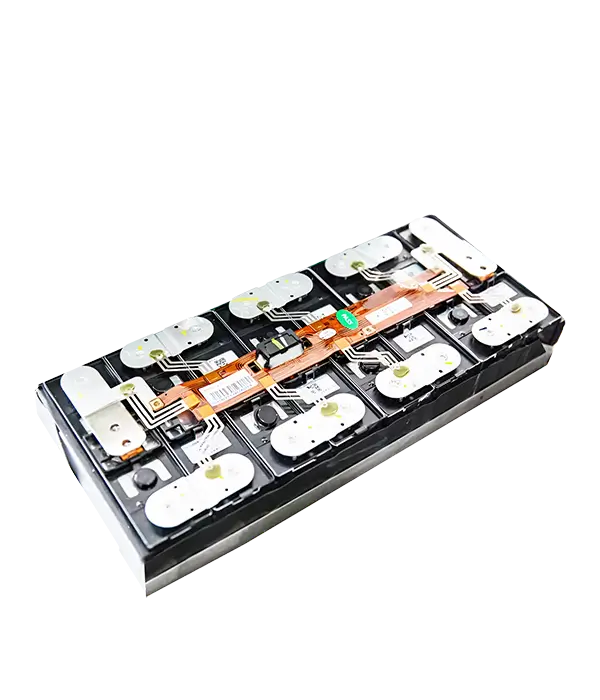
③ Battery Management Systems (BMS)
Flex PCB applications in BMS ensure robust, space-saving connections for EVs.
④ In-Car Lighting Systems
FPCs support dynamic lighting with greater design freedom.
⑤ Automotive Camera Modules
Flexible PCBs offer compact, reliable connections for high-resolution cameras.
⑥ Steering Wheel Control Systems
Integrated flex circuits improve responsiveness in control units.
⑦ Electric Seats and Folding Mirrors
FPCs replace bulky wiring in movable components.
⑧ Electronic Control Units (ECU)
Flex circuits enhance ECU compactness and diagnostics reliability.
⑨ Infotainment Systems
FPCs enable high-speed data transmission for touchscreens and audio modules.
6 Key Standards for Selecting Automotive Flexible Circuit Boards
① Automotive Certification Requirements
Ensure IATF 16949 compliance for automotive flex circuits.
② Material Selection
Made of high-performance materials for heat, chemicals, and vibration.
③ Reliability Testing
Validate through extreme temperature cycling and mechanical stress tests.
④ Layer Stackup and Design Flexibility
Optimize layers to balance flexibility and circuit integrity.
⑤ EMI Shielding and Signal Integrity
Employ conductive coatings to prevent interference.
⑥ Manufacturing Process Compliance
Verify that the manufacturing process for automotive PCBs includes cleanroom assembly and precision etching.
2025 Automotive Flexible Circuit Technology: 3 Major Trends
① Embedded Passive Components
Shrinks circuits with integrated resistors/capacitors.
② Irregular Shape Cutting
Maximizes Space-saving in compact layouts.
③ High-Frequency Materials
Supports automotive radar systems and high-speed communication.
FAQs
Q: What materials are used in automotive flexible PCBs?
A: Polyimide and polyester with high-temperature/chemical resistance.
Q: How do flex circuits improve reliability?
A: Through thermal management, vibration resistance, and reduced wiring failures.
Q: Are FPCs suitable for EVs?
A: Yes, especially for BMS, electronic control units (ECU), and motor controls.
Q: How does EMI shielding work?
A: Conductive coatings and ground planes protect signals from interference.
Get A Quote