Flex PCB in Industrial Automation: Driving Smart, Compact, and Cost-Effective Solutions
1. Introduction: The Role of Flexible PCBs in Industrial Automation
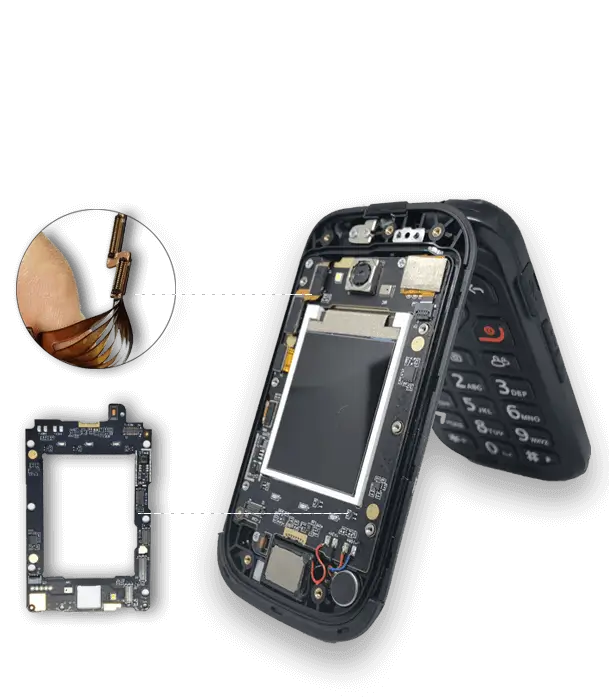
Modern industrial automation systems demand efficient and rugged electronic design.In sensor networks, we depend on flexible PCBs (flexible printed circuit boards). They come with several advantages over the traditional stiff circuit boards, such as flexible positioning and enhanced mechanical toughness.
- Importance of flexible circuit boards. As Downsizing and automation grow in electronics, flexible PCBs will help systems work in tough conditions. They will also fit in small spaces and support real-time operation in connected devices. Medical devices, consumer electronics, and automotive systems use them.
Flex PCBs offer design flexibility, meeting complex electrical needs. They improve system efficiency and performance, driving industrial automation development.
Scroll down to learn more application details!
2. Key Applications of Flexible PCBs in Industrial Automation
Robotics & Motion Control Systems
Flexible PCB technology supports complex motion in robotic arms and cobots. Fanuc uses tight pitch flex circuits in their servo motors. This allows for smooth movement and a steady flow of signals. It works well even when the cables face constant mechanical strain.
AGVs often use rigid flex circuits. They provide stability and flexibility for the moving parts on the factory floor.
Industrial IoT (IIoT) & Smart Sensor Systems
A predictive maintenance aspect and real-time feedback are key. Temperature, vibration, and proximity sensors all employ flexible circuit boards to record data with accuracy in harsh conditions.
Wireless modules embedded with flexible PCB layouts enable integration with 5G and LoRaWAN, key for scalable industrial networking.
Control Panels and Drives
- HMIs often use Flexible PCBs. They allow for thin and Tailored designs that make good use of the product’s internal space. Cost-effective flex circuits allow for easy mounting and fewer cabling errors for motor and servo drives.
However, the industry version of the flexible circuit, because of its flexibility and adaptability, and the complex industrial environment and different kinds of industrial equipment to adapt to the characteristics, with industrial automation and intelligence, is a very powerful and important support.
3. Technical Benefits of Flexible PCBs in Harsh Environments
Durability and High Reliability
Electronic components mounted on polyimide-based flexible PCBs operate stably under extreme temperatures (-40°C to 150°C).
Chemical-resistant coatings improve survival in oil-rich and high-humidity environments.
Reduced mechanical connectors improve overall system uptime.
Compact & Lightweight Designs
Flexible PCBs replace bulky wire harnesses, lowering weight and improving airflow.
3D layouts are ideal for devices like encoders and compact sensors in robotic joints.
Signal Integrity and EMI Control
High-density interconnects and impedance control reduce signal loss in high-speed applications.
Shielded layers in flexible circuit boards reduce EMI interference in complex automation tasks.
4. Emerging Trends in Flex PCB Use
AI & Edge Computing
Vision systems and AI-driven defect detection rely on flexible PCBs for localized processing.
Flexible PCB-enabled sensor nodes enhance responsiveness in edge computing systems.
Sustainable and Efficient Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing (3D-printed flexible circuit boards) speeds prototyping cycles.
- Use of recyclable substrates aligns with Recyclable goals in the electronics industry.
Cross-Sector Expansion
- From medical devices to consumer electronics, automation platforms increasingly adopt flexible PCB technologies to balance performance and volume flexibility.
7. FAQ: Flex PCBs in Industrial Automation
Q1: What is the cost difference between flexible and rigid PCBs??
A: Flexible PCBs may have a higher unit cost, but they save money in complex assemblies. They reduce the need for connectors, wiring, and labor.
Q2: Can flexible PCBs handle high-frequency applications?
A: Yes. RF modules and high-speed data lines benefit from flexible circuit board designs with impedance-controlled traces and shielding.
Q3: What are rigid flex circuits best used for?
A: AGVs and control panels use rigid flex circuits to achieve stability and mobility.
A: In addition to industrial automation, medical devices, consumer electronics, and aerospace systems heavily rely on flexible circuit technology.
Q5: How does flex PCB technology improve device performance?
- A: By reducing bulky connectors and allowing design flexibility, it enhances durability, reduces noise, and increases the integration of compact electronic components.
Q6: What affects the cost of flexible PCB manufacturing?
A: Layer count, copper thickness, surface finish, and complexity of shape all influence final pricing. However, flexible PCB manufacturing processes continue to advance, reducing costs over time.
Q7.How to choosing the Right Flex PCB Supplier?
Look for suppliers who specialize in industrial and medical device applications. Key traits include:
IPC-6013, UL, and ISO 13485 certifications
In-house testing for high-density layouts
Expertise in hybrid rigid flex circuit development
Strong R&D for emerging electronics industries use cases
Q8: Flex PCB Manufacturing: What Engineers Need to Know
Flexible PCB manufacturing processes include:
Photo imaging and etching for ultra-fine traces
Laser drilling for microvias and multilayer connections
Lamination of rigid-flex combinations for hybrid mechanical behavior
- Automated testing to ensure resistance to heat, chemicals, and Ruggedized design-for-manufacturability (DFM) is essential to achieving both performance and cost targets.
Get A Quote